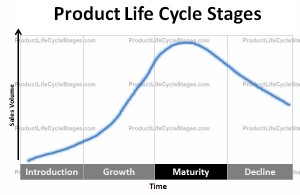
 After the Introduction and Growth stages, a product passes into the Maturity stage. The third of the product life cycle stages can be quite a challenging time for manufacturers. In the first two stages companies try to establish a market and then grow sales of their product to achieve as large a share of that market as possible. However, during the Maturity stage, the primary focus for most companies will be maintaining their market share in the face of a number of different challenges.
After the Introduction and Growth stages, a product passes into the Maturity stage. The third of the product life cycle stages can be quite a challenging time for manufacturers. In the first two stages companies try to establish a market and then grow sales of their product to achieve as large a share of that market as possible. However, during the Maturity stage, the primary focus for most companies will be maintaining their market share in the face of a number of different challenges.
Challenges of the Maturity Stage
- Sales Volumes Peak: After the steady increase in sales during the Growth stage, the market starts to become saturated as there are fewer new customers. The majority of the consumers who are ever going to purchase the product have already done so.
- Decreasing Market Share: Another characteristic of the Maturity stage is the large volume of manufacturers who are all competing for a share of the market. With this stage of the product life cycle often seeing the highest levels of competition, it becomes increasingly challenging for companies to maintain their market share.
- Profits Start to Decrease: While this stage may be when the market as a whole makes the most profit, it is often the part of the product life cycle where a lot of manufacturers can start to see their profits decrease. Profits will have to be shared amongst all of the competitors in the market, and with sales likely to peak during this stage, any manufacturer that loses market share, and experiences a fall in sales, is likely to see a subsequent fall in profits. This decrease in profits could be compounded by the falling prices that are often seen when the sheer number of competitors forces some of them to try attracting more customers by competing on price.
Benefits of the Maturity Stage
- Continued Reduction in Costs: Just as economies of scale in the Growth stage helped to reduce costs, developments in production can lead to more efficient ways to manufacture high volumes of a particular product, helping to lower costs even further.
- Increased Market Share Through Differentiation: While the market may reach saturation during the Maturity stage, manufacturers might be able to grow their market share and increase profits in other ways. Through the use of innovative marketing campaigns and by offering more diverse product features, companies can actually improve their market share through differentiation and there are plenty of product life cycle examples of businesses being able to achieve this.
Product Life Cycle Management in the Maturity Stage
The Maturity stage of the product life cycle presents manufacturers with a wide range of challenges. With sales reaching their peak and the market becoming saturated, it can be very difficult for companies to maintain their profits, let alone continue trying to increase them, especially in the face of what is usually fairly intense competition. During this stage, it is organizations that look for innovative ways to make their product more appealing to the consumer that will maintain, and perhaps even increase, their market share.
Next: Decline Stage