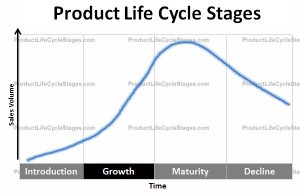
 The Growth stage is the second of stages in the product life cycle, and for many manufacturers this is the key stage for establishing a product’s position in a market, increasing sales, and improving profit margins. This is achieved by the continued development of consumer demand through the use of marketing and promotional activity, combined with the reduction of manufacturing costs. How soon a product moves from the Introduction stage to the Growth stage, and how rapidly sales increase, can vary quite a lot from one market to another.
The Growth stage is the second of stages in the product life cycle, and for many manufacturers this is the key stage for establishing a product’s position in a market, increasing sales, and improving profit margins. This is achieved by the continued development of consumer demand through the use of marketing and promotional activity, combined with the reduction of manufacturing costs. How soon a product moves from the Introduction stage to the Growth stage, and how rapidly sales increase, can vary quite a lot from one market to another.
Challenges of the Growth Stage
- Increasing Competition: When a company is the first one to introduce a product into the market, they have the benefit of little or no competition. However, when the demand for their product starts to increase, and the company moves into the Growth phase of the product life cycle, they are likely to face increased competition as new manufacturers look to benefit from a new, developing market.
- Lower Prices: During the Introduction stage, companies can very often charge early adopters a premium price for a new product. However, in response to the growing number of competitors that are likely to enter the market during the Growth phase, manufacturers may have to lower their prices in order to achieve the desired increase in sales.
- Different Marketing Approach: Marketing campaigns during the Introduction stage tend to benefit from all the buzz and hype that surrounds the launch of a new product. But once the product becomes established and is no longer ‘new’, a more sophisticated marketing approach is likely to be needed in order to make the most of the growth potential of this phase.
Benefits of the Growth Stage
- Costs are Reduced: With new product development and marketing, the Introduction stage is usually the most costly phase of a product’s life cycle. In contrast, the Growth stage can be the most profitable part of the whole cycle for a manufacturer. As production increases to meet demand, manufacturers are able to reduce their costs through economies of scale, and established routes to market will also become a lot more efficient.
- Greater Consumer Awareness: During the Growth phase more and more consumers will become aware of the new product. This means that the size of the market will start to increase and there will be a greater demand for the product; all of which leads to the relatively sharp increase in sales that is characteristic of the Growth stage.
- Increase in Profits: With lower costs and a significant increase in sales, most manufacturers will see an increase in profits during the Growth stage, both in terms of the overall amount of profit they make and the profit margin on each product they sell.
Product Life Cycle Management
The standard Product Life Cycle Curve typically shows that profits are at their highest during the Growth stage. But in order to try and ensure that a product has as long a life as possible, it is often necessary for manufacturers to reinvest some of those profits in marketing and promotional activity during this stage, to help guarantee continued growth and reduce the threat from the competition.
Next: Maturity Stage